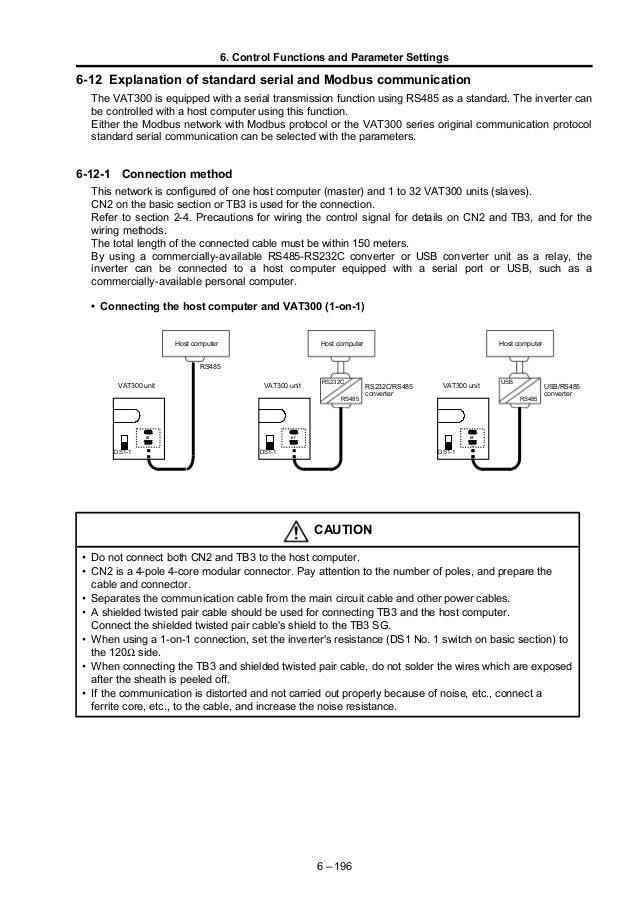
Rs485 Serial Communication Protocol Training Manual
Serial communication. RS-232 and RS-485 protocolsAll the Technosoft drives/motors can communicate via RS-232. Some of them also accept RS-485 as a substitute for RS-232. In the following paragraphs, the terminology serial communication refers to the features common to both RS-232 and RS-485. The terminology RS-232 communication or RS-485 communication is used to features that are specific for one or the other.The RS-232 communication is point-to point, full duplex, and enables you to link 2 devices.
A typical example is when you connect your PC with a Technosoft drive/motor.Use the RS-232 communication if you want to. D)Control several drives/motors connected via CAN-bus, with commands sent from your host which is connected via RS-232 with one of themIn cases c) and d), the Technosoft drive/motor connected to the host acts as a relay axis (see for details).The RS-485 communication is multi-point, half duplex, and enables you to link up to 32 drives/motors in a network.
Rs485 Serial Protocol
In an RS-485 network, at one moment only one device is allowed to send data. If two devices start by mistake to transmit in the same time, both transmissions are corrupted. Therefore for a correct operation, in an RS-485 network it is mandatory to have a master, which controls the transmission. Put in other words, only the master can initiate a transmission, while all the other devices from the network may transmit only when the master asks them to provide some data. Normally you should set as master your host.Use the RS-485 communication if you want to. Serial communication settings and message encapsulationThe Technosoft drives communicate serially using 8 data bits, 2 stop bits, no parity at the following baud rates: 9600 (default after reset), 19200, 38400, 56600 and 115200.
The messages exchanged through serial communication are encapsulated in the following format:Serial message structure – TML Instruction encapsulationThe message length byte contains the total number of bytes of the message minus 2. Put in other words, the length byte value is the number of bytes of the: Axis/group ID Code (2bytes), the Operation Code (2 bytes) and the Data words (variable from 0 to 8 bytes). The Checksum byte is the sum modulo 256 of all the bytes of the message except the checksum byte itself.Message types on serial communicationThe serial communication protocol is based on 3 types of messages imposed by the nature of the TML commands encapsulated.Type C: Messages sent by a drive/motor to a host without being requested by the host.
These messages may be sent either when a specific condition occurs or following the execution of the TML command (see for details)The next paragraphs present an example of each message type.Example 1 – Type A Message: A host is connected to a drive/motor via RS-232 and sends the TML instruction “KPP = 5” (set proportional part of the position controller with value 5). The axis ID of host and of the drive/motor are 255 = 0FFh. The Axis ID code and the TML instruction binary code are:Axis ID code + Binary code of TML Instruction KPP = 5 sent to axis 255Remark: Use to get the binary code of TML instructionsThe host must send a serial message with the following contents:Serial message: TML Instruction KPP = 5 sent to axis 255The drive/motor will return a byte 0x4F as confirmation that the message was received OK. (See below the RS-232 and RS-485 protocols description for details)Remarks. B)If the host is connected via RS-485 with a drive, the 2 devices must have different axis ID values.
For example if the host axis ID = 255 and the drive ID = 1, the message is the same as in remark a)Example 2 – Type B Message: A host is connected to a drive via RS-232 and wants to get the value of the KPP (proportional term of the position controller) parameter from the drive. KPP address in TML data memory is 025Eh. The ID of the host and the drive/motor are 255 = 0FFh. The host sends a “GiveMeData” request and the drive/motor answers with a “TakeData” message. “TakeData”: Axis ID Code – 0FF0h instead of 0FF1h (Host bit = 0) and Sender Axis ID Code – 0010h instead of 0FF0h;Example 3 – Type C Message: A host is connected to a drive via RS-232 and wants to be informed when the programmed motion is completed. The axis ID of the host and the drive/motor are 255 = 0FFh. A Type C message is a “TakeData2” message sent without a “GiveMeData2” request.
It includes the following information:“TakeData2” - Message descriptionThe destination axis is provided by the TML variable MASTERID, according with formula: MASTERID = host axis ID. 16 + 1. In this example, the 8-bit host axis ID = 255, hence MASTERID = 16. 255 + 1 = 4081 (0xFF1). In the case of a Type C message, the “TakeData2” can return.The 16-bit or 32-bit TML data requested to be sent with the TML command SEND.Remark: Use to get the addresses for the above TML data. Note that the SRL and SRH status registers may also be accessed as a single 32-bit variable named SR32.The bit selection is done via 3 masks, one for each register, set in TML parameters: SRLMASK, SRHMASK, MERMASK. A bit set in a mask, enables a message transmission when the same bit from the corresponding register changes.
In this example, the motion complete condition is signaled by setting SRL. To activate automatic sending of a “TakeData2” whenever SRL. 10 changes, set SRLMASK = 0x0400.If SRH = 0x201 and SRL = 0x8400, after SRL. 10 goes from 0 to 1, the host gets a “TakeData2” message with the following contents:Serial message: “TakeData2” with status registers SRL and SRH from axis 255Remark: A “TakeData2” message with SRL.10=1 signals that the last programmed motion is completed. A “TakeData2” message with SRL.10=0 signals that a new motion has started and may be used as a confirmation for the last motion command.RS-232 communication protocolThe RS-232 protocol is full duplex, allowing simultaneous transmission in both directions. After each command (Type A or B) sent by the host, the drive will confirm the reception by sending one acknowledge- O k byte. This byte is: ‘O’ (ASCII code of capital letter “o”, 0x4F).
If the host receives the ‘O’ byte, this means that the drive has received correctly (checksum verification was passed) the last message sent, and now is ready to receive the next message.Remark: If the destination axis for the message is not the axis connected with the host via RS-232 (e.g. The relay axis), but another axis connected with the relay axis via CAN-bus, the reception of the acknowledge- O k byte from the relay axis doesn’t mean that the message was received by the destination axis, but just by the relay axis. Depending on the CAN-bus baud rate and the amount of traffic on this bus, the host may need to consider introducing a delay before sending the next message to an axis connected on the CAN-bus. This delay must provide the relay axis the time necessary to retransmit the message via CAN-bus.If any error occurs during the message reception, for example the checksum computed by the drive axis doesn’t match with the one sent by the host, the drive will not send the acknowledge- O k byte.
If the host doesn’t receive any acknowledge byte for at least 2ms after the end of the checksum byte transmission, this means that at some point during the last message transmission, one byte was lost and the synchronization between the host and the relay axis is gone. In order to restore the synchronization the host should do the following. C)Wait the answer message from the drive/motor (as in Example 2, in case of a “Take Data” answer)When the relay axis returns an answer message it doesn’t expect to receive an acknowledge byte from the host. It is the host task to monitor the communication. If the host gets the response message with a wrong checksum, it is the host duty to send again the data request.RS-485 communication protocolThe RS-485 protocol is half duplex. If two devices start by mistake to transmit in the same time, both transmissions are corrupted. Therefore for a correct operation, in an RS-485 network it is mandatory to have a master, which controls the transmission.
This means that only the master can initiate a transmission, while all the other devices from the network may transmit only when the master asks them to provide some data. Usually you should set as master your host.After each command (Type A or B) sent by the host to one drive, the drive will confirm the reception by sending one acknowledge- O k byte. This byte is: ‘O’ (ASCII code of capital letter “o”, 0x4F).
If the host receives the ‘O’ byte, this means that the drive has received correctly (checksum verification was passed) the last message sent, and now is ready to receive the next message.The acknowledge- O k byte is not sent when the host broadcasts a message to a group of drives.If any error occurs during the message reception, for example if the checksum computed by the drive axis doesn’t match with the one sent by the host, the drive will not send the acknowledge- O k byte. If the host doesn’t receive any acknowledge byte for at least 2ms after the end of the checksum byte transmission, this means that at some point during the last message transmission, one byte was lost and the synchronization between the host and the relay axis is gone. In order to restore the synchronization the host should do the following.
A large number of current electronic equipment communicate with computers via serial ports. RS-485 is one of the legacy serial interfaces still widely applied these days. Extremely common in industrial automation, RS-485 is used in industrial networks, including Modbus, Profibus DP, ARCNET, BitBus, WorldFip, LON, Interbus, as well as many other non-standard networks.
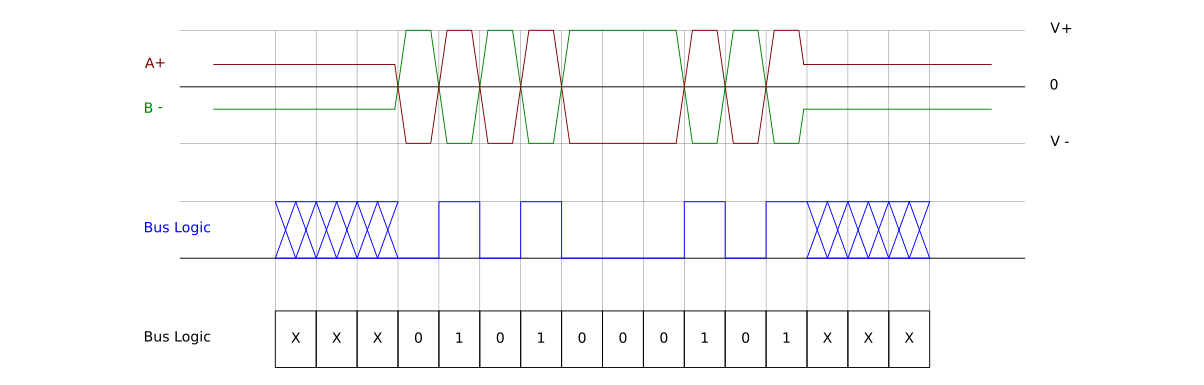
At present, serial RS-485 port is rightfully considered to be the most efficient way of serial communication. So, let’s find out why RS-485 communication remains that popular and what is the simplest way to monitor and test this common interface. Contents.What is RS-485?RS-485 (currently known as EIA/TIA-485) is a standard interface of the physical layer of communication, a signal transmission method, the 1st level of the Open System Interconnection model. RS-485 has been created in order to expand the physical capabilities of RS-232 interface.The serial EIA-485 connection is done using a cable of two or three wires: a data wire, a wire with inverted data, and, often, a zero wire (ground, 0 V). This way, transmitters and receivers exchange data via a twisted-pair cable of 22 or 24 AWG solid wires. The main idea here is to transport one signal over two wires.
While one wire transmits the original signal, the other one transports its inverse copy. Such transmission method provides high resistance to common mode interference.
The twisted-pair cable that serves as a transmission line can be shielded or unshielded. RS-485 communication: main featuresDespite the wide variety of modern alternative solutions, today RS-485 technology remains the basis of many communication networks.
The major advantages of RS-485 interface are:. Two-way data exchange via one twisted pair of wires;.
support for several transceivers connected to the same line, i.e., the ability to create a network;. long length of the communication line;. high transmission speed.Now, let’s take a closer look at the main characteristics of RS-485 communication:. Bi-directional half-duplex data transmission. Serial data stream can be transported in one direction, data transfer to the other side requires using a transceiver.
A transceiver (commonly referred to as 'driver') is a device or an electrical circuit that forms a physical signal on the transmitter side. Symmetrical communication channel.
Receiving or transmitting data requires two equivalent signal wires. The wires are used to exchange data in both directions (alternatively). With the help of a twisted pair cable, the symmetrical channel significantly increases the stability of a signal and suppresses electromagnetic radiation generated by the useful signal. Multi-pointing. RS-485 communication line can work with multiple receivers and transceivers connected. At the same time, one transmitter and several receivers can be attached to one communication line at a time.
All the other transmitters that need to be connected should wait until the communication line is free for data transmission.How to test RS-485 ports with Serial Port MonitorThe EIA/TIA-485 standard is widely used in industrial applications that work over long distances and require high speeds of data transmission. The interface is particularly useful for connecting serial devices in noisy environments like process control plants, utilities sites, and factories.RS-485 port is embedded on various devices, including low-speed modems, programmable logic controllers, computer numerically controlled machine tools, point of sale terminals, metering instruments, large special automated machines, and other equipment.So, it should come as no surprise that specialists working with RS-485 ports may need to test the serial interfaces in order to identify and resolve problems that may appear in RS-485 networks. More than that, programmers who develop industrial serial applications may also require a specialized tool for reading and monitoring serial ports their apps communicate with.Thankfully, there’s a dedicated RS-485 test software that is designed to make it as simple as possible to monitor and analyze RS-485 port activity. Packed with a slew of advanced features, the software doesn’t need additional hardware to track and record data going through monitored serial ports.
Core functionality of RS-485 test toolThe key capabilities of RS485 communication software (SPM) include:. Connecting to a COM port any time you need it even if the port is already used by another app. Once you start monitoring a required RS-485 interface, all data transmitted through it is shown in real time. Thanks to this option, you can timely resolve any problem that arises in your serial communication network.
Rs485 Serial Communication
Monitoring multiple COM ports at a time. Whether you need to analyze one, two, or several RS-485 ports, it’s possible to do this in one monitoring session. With that, the captured data will be saved to a single log. Simulating serial communication.
The Terminal mode option allows you to emulate sending particular data in different formats (string, binary, octal, decimal, hexadecimal, mixed). The RS-485 loopback feature offered by the software is particularly useful for sessions comparison.How-to guideWhether you need to remotely monitor a controller fitting RS-485 port, check the reaction of a particular serial device to certain data, or analyze the activity of all RS-485 interfaces your system deploys, here is how you can do this with Serial Port Monitor:To start, the software and install it on your computer. Launch the app in order to start a new monitoring session:. In the main menu of the app select Session - New session. Alternatively, you can hit ‘New’ on the main toolbar or press CTRL+N. As a result, you’ll get the ‘New monitoring session’ window.
Now, decide on how you’d like the captured data to be displayed and choose the desired visualizer. There are Table, Line, Dump, Terminal, and Modbus views.
As an option, you can use them all simultaneously. Next, depending on where you want your monitoring session to be started, choose between the ‘Start monitoring now’ and ‘Start in new window’ options. In the ‘Capture options’ select the type of events you’d like to track (Create/Close, Read/Write, Device Control.). Finally, hit ‘Start monitoring’.
Now you can easily catch and analyze data transmitted via a required RS-485 port.If it’s necessary to save a session, you should go to the main menu and select “Session - Save session/Save session As”. Or, click “Save” on the main toolbar, or press CTRL+S.Find more information.
Download all chapters of Solutions Manual for Fundamentals of Investing 10th Edition by Gitman. Product Description. Solution Manual Fundamentals of Investing 10th Edition Gitman. Table of Contents. Chapter 1: The Investment Environment Chapter 2:. 